CI/CD and GitOps
Overview
wasmCloud components are distributed as OCI artifacts, so a CI/CD pipeline for wasmCloud follows a familiar pattern: build .wasm binaries, push them to an OCI registry, and update Kubernetes manifests to reference the new image.
The wasmCloud project provides a set of official GitHub Actions that handle building components, publishing to OCI registries, and generating supply-chain attestations. For teams using GitOps, Argo CD or Flux can close the loop by reconciling Kubernetes state with a Git repository.
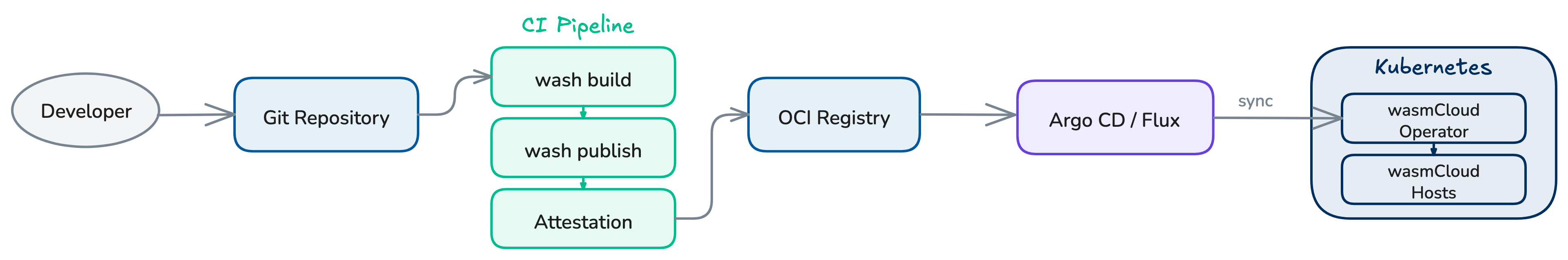
wasmCloud GitHub Actions
wasmCloud provides four GitHub Actions for CI pipelines:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
wasmCloud/setup-wash-action | Installs the wash CLI on the runner |
wasmcloud/actions/setup-wash-cargo-auditable | Configures cargo-auditable to embed SBOM data in Rust builds |
wasmcloud/actions/wash-build | Builds a Wasm component, outputs the path to the built artifact |
wasmcloud/actions/wash-oci-publish | Publishes a component to an OCI registry with optional attestation and SBOM |
setup-wash-action
The setup-wash-action installs wash, adds it to PATH, caches the binary, and installs the wasm32-wasip2 Rust target.
- uses: wasmCloud/setup-wash-action@main
with:
wash-version: "wash-v2.0.0-rc.7" # version to install (default: wash-v2.0.0-rc.7)setup-wash-cargo-auditable
The setup-wash-cargo-auditable action installs cargo-auditable and cargo-audit, then configures .wash/config.yaml so that wash build uses cargo auditable build under the hood. This embeds dependency metadata in the compiled binary for later SBOM extraction.
A Cargo project (Cargo.toml) must already exist in the working directory before calling this action, as it reads the package name to determine the component output path.
- uses: wasmcloud/actions/setup-wash-cargo-auditable@main
with:
working-directory: "." # directory containing the project (default: .)wash-build
The wash-build action runs wash build --output json and exposes the path to the built component as a step output.
- id: build
uses: wasmcloud/actions/wash-build@main
with:
working-directory: "." # directory containing the project (default: .)Output: steps.build.outputs.component_path — path to the built .wasm file.
wash-oci-publish
The wash-oci-publish action pushes the built component to an OCI registry. When attestation is enabled, the action generates build provenance and an SBOM (converted from CycloneDX to SPDX format).
- uses: wasmcloud/actions/wash-oci-publish@main
with:
component_path: ${{ steps.build.outputs.component_path }} # required
registry: ghcr.io # default: ghcr.io
attestation: "true" # default: false
image_tags: "latest,v1.0.0,${{ github.sha }}" # default: branch nameWhen attestation is enabled, the workflow needs the following permissions. See Supply chain security for details.
permissions:
contents: write
packages: write
attestations: write
id-token: writeAttestation
When attestation is enabled, the wash-oci-publish action generates cryptographically signed metadata that links a published artifact back to the source code, build environment, and dependency tree that produced it. This enables consumers to verify that an artifact was built from a specific commit in a trusted CI pipeline.
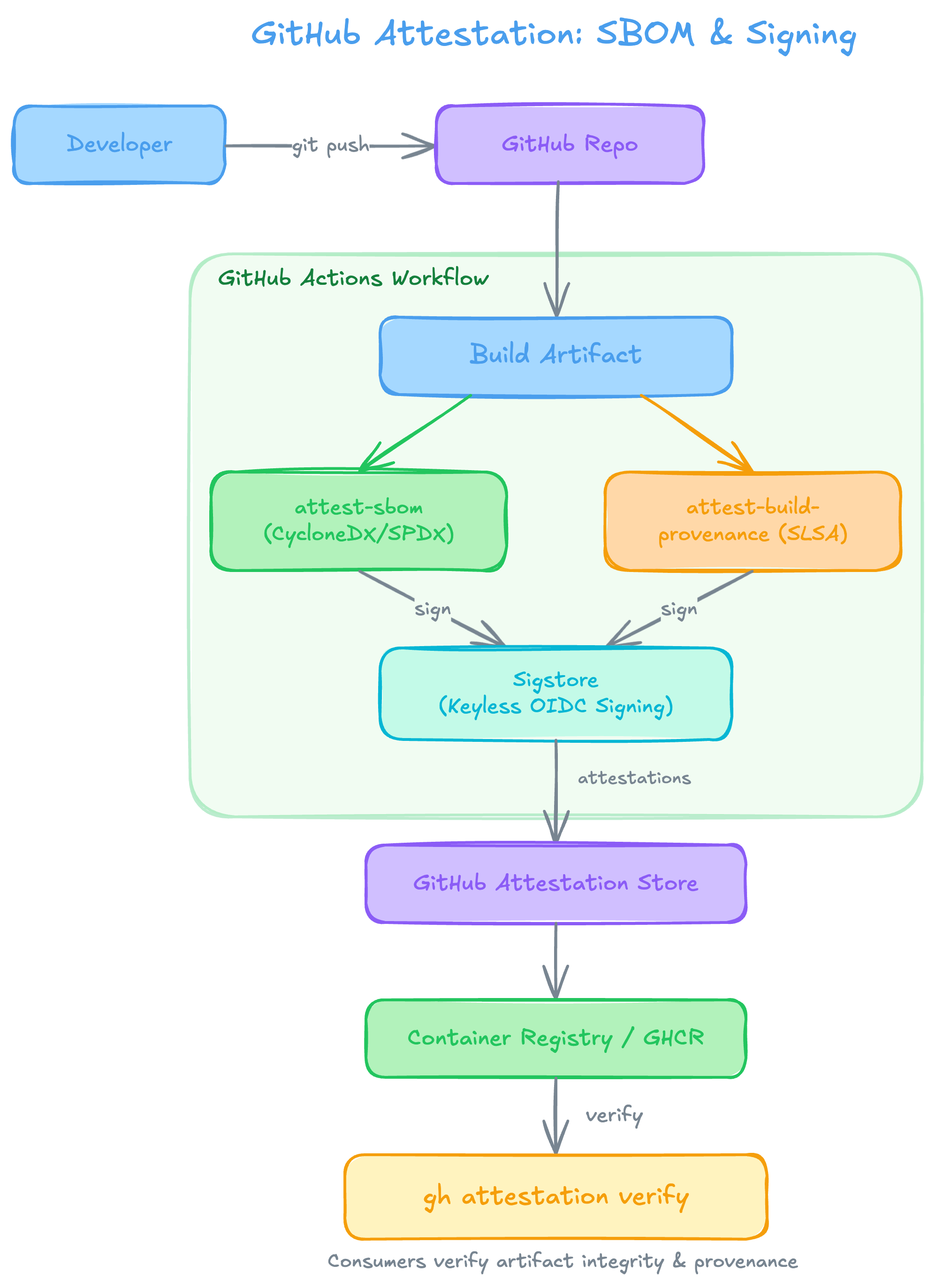
The attestation flow works as follows:
- A developer pushes code to a GitHub repository, triggering a GitHub Actions workflow.
- The workflow runs
wash build(withcargo-auditable) to compile the component, embedding dependency metadata in the binary. - Two attestations are generated in parallel:
attest-sbomextracts a CycloneDX SBOM from the binary, converts it to SPDX format, and creates an SBOM attestation.attest-build-provenancegenerates SLSA build provenance, recording where, how, and from what source the artifact was built.
- Both attestations are signed via Sigstore using keyless OIDC signing—no manual key management required.
- The signed attestations are stored in the GitHub Attestation Store and associated with the published artifact in the container registry (e.g., GHCR).
- Consumers can run
gh attestation verifyto confirm the artifact's integrity and provenance before deploying it.
Example: Build and publish pipeline
The following GitHub Actions workflow builds a Rust-based Wasm component with auditable dependency metadata, publishes it to GitHub Container Registry, and generates supply-chain attestations:
name: Build and Publish Component
on:
push:
tags:
- "v*"
permissions:
contents: write
packages: write
attestations: write
id-token: write
jobs:
build-and-publish:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v6
- name: Setup wash CLI
uses: wasmCloud/setup-wash-action@main
- name: Setup cargo-auditable
uses: wasmcloud/actions/setup-wash-cargo-auditable@main
- name: Build component
id: build
uses: wasmcloud/actions/wash-build@main
- name: Publish component
uses: wasmcloud/actions/wash-oci-publish@main
with:
component_path: ${{ steps.build.outputs.component_path }}
registry: ghcr.io
attestation: "true"
image_tags: "latest,${{ github.ref_name }}"This pipeline triggers on version tags (e.g. v1.0.0). The published image will be tagged with both latest and the Git tag.
GitOps with Argo CD
For production deployments, a GitOps workflow keeps Kubernetes state in sync with a Git repository. Argo CD is a popular GitOps tool for Kubernetes and pairs well with the wasmCloud operator.
Two-application pattern
A common pattern uses two Argo CD Applications:
- Infrastructure Application — deploys the wasmCloud platform (operator, NATS, hosts) from the Helm chart.
- Workloads Application — deploys
WorkloadDeploymentmanifests from a dedicated Git repository.
This separation lets infrastructure and workload teams operate independently, each managing their own deployment cadence.
Example Argo CD Applications
Infrastructure Application — installs the wasmCloud operator via Helm:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: wasmcloud-platform
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
chart: runtime-operator
repoURL: ghcr.io/wasmcloud/charts
targetRevision: v2-canary
helm:
releaseName: wasmcloud
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: default
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: trueWorkloads Application — syncs WorkloadDeployment manifests from a Git repository:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: wasmcloud-workloads
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/<org>/wasmcloud-workloads.git
targetRevision: main
path: manifests
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: default
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: trueAutomating manifest updates
After the CI pipeline publishes a new component image, a second workflow job can update the WorkloadDeployment manifest in the workloads repository and open a pull request:
update-manifests:
needs: build-and-publish
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v6
with:
repository: <org>/wasmcloud-workloads
token: ${{ secrets.WORKLOADS_REPO_TOKEN }}
- name: Update image tag
run: |
sed -i "s|image: ghcr.io/<org>/my-component:.*|image: ghcr.io/<org>/my-component:${{ github.ref_name }}|" \
manifests/my-component.yaml
- name: Create pull request
uses: peter-evans/create-pull-request@v7
with:
title: "Update my-component to ${{ github.ref_name }}"
commit-message: "chore: update my-component to ${{ github.ref_name }}"
branch: "update-my-component-${{ github.ref_name }}"Once merged, Argo CD detects the change and rolls out the new version automatically.
This pattern works with any GitOps tool that watches a Git repository for changes, including Flux.
Supply chain security
The wasmCloud GitHub Actions support a full supply-chain security pipeline using cargo-auditable, CycloneDX, and GitHub's built-in attestation actions.
The attestation flow works as follows:
setup-wash-cargo-auditableconfigurescargo-auditablevia.wash/config.yamlso that dependency metadata is embedded in the compiled binary duringwash build.wash-oci-publish(withattestation: "true") extracts the embedded metadata and generates attestations:- Extracts a CycloneDX SBOM from the binary using
auditable2cdx - Converts the SBOM to SPDX format using
cyclonedx-cli - Generates an SBOM attestation via
actions/attest-sbom - Generates build provenance via
actions/attest-build-provenance
- Extracts a CycloneDX SBOM from the binary using
For attestation to work, the workflow must include the following permissions block:
permissions:
contents: write # required for attestation uploads
packages: write # required for OCI registry push
attestations: write # required for attestation creation
id-token: write # required for OIDC token (provenance signing)Without all four permissions, the attestation steps will fail. If you don't need attestation, you can omit these permissions and set attestation: "false" (the default).